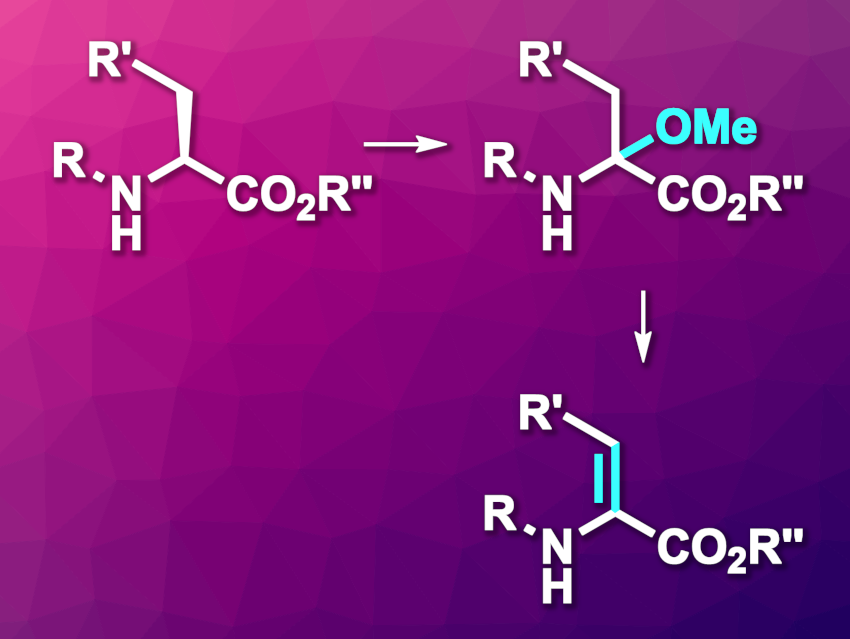
α,β-Dehydroamino acids (dhAAs) can take part, e.g., in addition reactions. This can be used, for example, for the late-stage functionalization of peptides that contain dhAAs. However, the synthesis of some dhAAs can be challenging.
Mathias Christmann, Free University Berlin, Germany, and colleagues have developed an electrochemical method that provides access to protected dhAA derivatives (general reaction pictured). The team started from tert-butyl or benzyl carbamates (i.e., Boc- or Cbz-protected substrates), which underwent an α-methoxylation mediated by NaCl, using LiClO4 as the electrolyte and MeOH as the solvent in an undivided electrochemical cell with graphite electrodes (product pictured above in the top right corner).
The resulting α-methoxylated amino acid derivatives were then converted to dhAA derivatives (pictured above in the bottom right corner) via the elimination of the methoxy group. For this, the researchers used pyridinium para-toluenesulfonate (PPTS) as an acidic catalyst. The team found that the developed approach can be used on a gram scale to access different carbamate-protected dhAAs. They highlight the simple setup, using low-cost graphite electrodes and NaCl as a mediator.
- Electrosynthesis of Protected Dehydroamino Acids,
Marcel Gausmann, Nadine Kreidt, Mathias Christmann,
Org. Lett. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.3c00403