Quinoids are a class of chemical compounds that are derived from quinone. This type of compound has applications, e.g., in organic semiconducting, magnetic, and optical materials. Quinoidal molecules with para– and ortho-quinodimethane scaffolds, for example, are interesting research targets. They can be prepared, e.g., via a dehydrogenation of hydrocarbon precursors or via a reduction of dications.
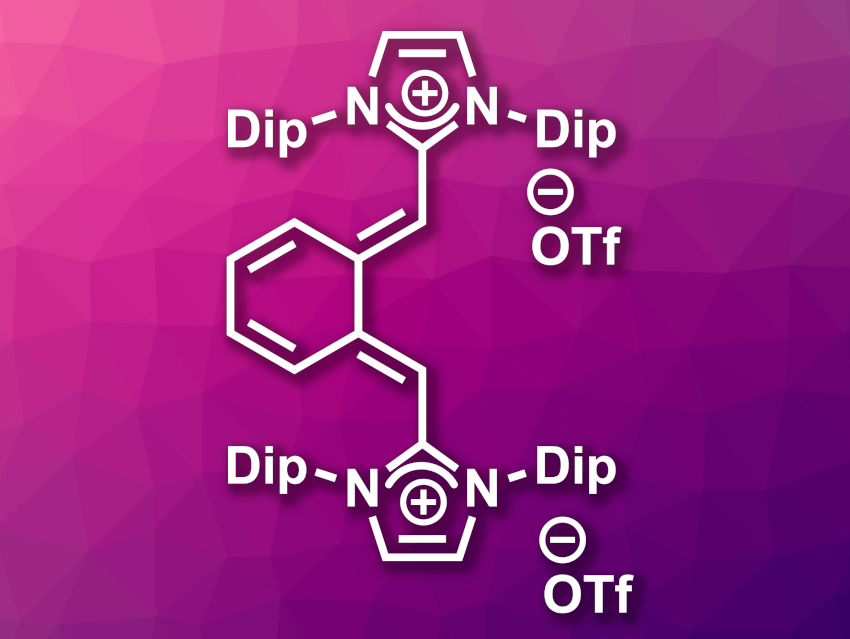
Swapan K. Pati, Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Bangalore, India, Carola Schulzke, University of Greifswald, Germany, Holger Braunschweig, University of Würzburg, Germany, Cem B. Yildiz, University of Aksaray, Turkey, Anukul Jana, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research Hyderabad, India, and colleagues have developed a method for the synthesis of diimidazolium para– and ortho-quinodimethane derivatives (example pictured). The team’s approach is based on the two-electron oxidation of bis–N-heterocyclic olefins linked via π-conjugated aromatic spacers. They used para-phenylene, ortho-phenylene, para-tetrafluorophenylene, and para-anthracene-bridged bis–N-heterocyclic olefins as substrates.
The bis–N-heterocyclic olefins were oxidized using two equivalents of AgOTf. According to the researchers, the products represent a new class of quinoidal compounds and are stable in the presence of air and moisture. Depending on the π-conjugated spacer, the team observed either two one-electron or one two-electron redox transitions between the bis-N-heterocyclic olefins and the diimidazolium quinodimethanes in cyclic voltammetry (CV) experiments. The work might be useful as a starting point for further research into this new class of quinoidal compounds.
- Air and Moisture Stable para– and ortho-Quinodimethane Derivatives Derived from bis-N-Heterocyclic Olefins,
Subhadip Jana, Benedict J. Elvers, Sebastian Pätsch, Pallavi Sarkar, Ivo Krummenacher, Mithilesh Kumar Nayak, Avijit Maiti, Nicolas Chrysochos, Swapan K. Pati, Carola Schulzke, Holger Braunschweig, Cem B. Yildiz, Anukul Jana,
Org. Lett. 2023.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.2c03993


Congratulations to all.