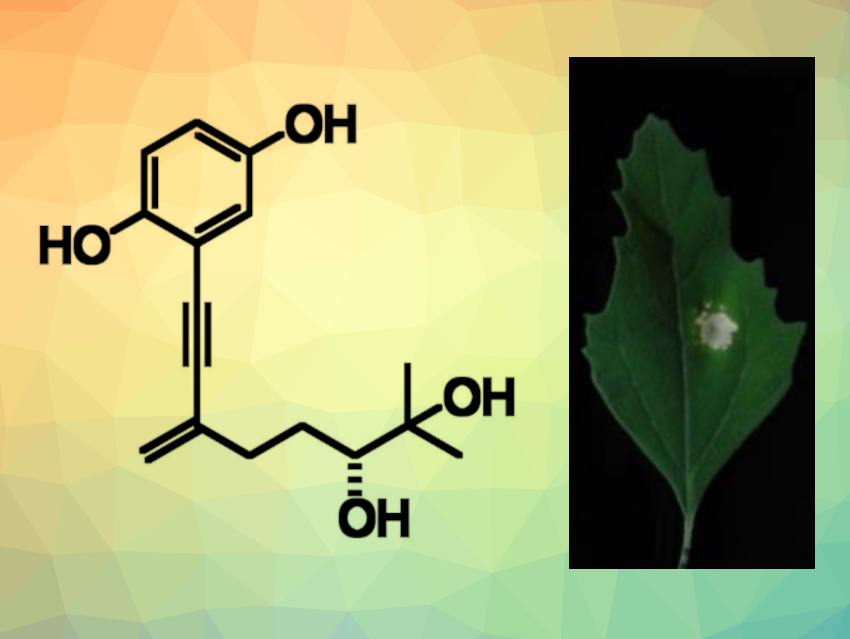
Foeniculoxin (pictured) is a phytotoxin produced by the fungus Phomopsis foeniculi, which can infect fennel plants. The fungus can affect the fennel’s leaves and stem, which can kill the plant. So far, there had been no reported total synthesis of foeniculoxin and no detailed studies of the compound’s phytotoxicity.
Makoto T. Fujiwara, Toyonobu Usuki, Sophia University, Tokyo, Japan, and colleagues have performed a total synthesis of foeniculoxin. The team started from trimethylsilylacetylene, which was converted to a cumulene. This cumulene was reacted with an enone obtained from 1-methoxyallene to give an enyne building block. The second building, an aryl iodide, was prepared from hydroquinone. A Sonogashira cross-coupling reaction was then used to combine the two building blocks. This was followed by the removal of a trimethylsilyl group and an asymmetric Corey-Bakshi-Shibata reduction, which introduced the target compound’s stereocenter.
The synthesis of foeniculoxin was achieved in five steps from trimethylsilylacetylene with 19 % overall yield. The team determined the compound’s absolute configuration using the advanced Mosher’s method. The researchers also studied the phytotoxicity of the product by injecting it into leaves of Chenopodium album (white goosefoot) and Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress). They found that foeniculoxin induced the death of leaf cells in both plants. Using fluorescence imaging, they observed the formation of abnormalities at the cellular level before the formation of dead spots on thale cress leaves.
- Total Synthesis, Absolute Configuration, and Phytotoxic Activity of Foeniculoxin,
Akane Yamagishi, Yuki Egoshi, Makoto T. Fujiwara, Noriyuki Suzuki, Tohru Taniguchi, Ryuuichi D. Itoh, Yumiko Suzuki, Yoshiro Masuyama, Kenji Monde, Toyonobu Usuki,
Chem. Eur. J. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.202203396