Many proteins contain patterns of sugar molecules (glycans) and are made of several aggregated subunits. This glycosylation and oligomerization has a decisive influence on protein function and must be considered in biopharmaceutical development. Carol V. Robinson and Di Wu, University of Oxford, UK, have introduced an approach based on native top-down mass spectroscopy (MS) that can be used to analyze the interplay between glycosylation and oligomerization in various therapeutic hormones and cytokines.
Native Top-Down Mass Spectrometry
In conventional MS, molecules break into fragments, but native MS makes it possible to examine folded protein oligomers bound to glycans. In the top-down method, the oligomers are subsequently separated by means of a gas-phase dissociation and measured. In a final step, gas-phase fragmentation is used to split off and analyze the glycans. For a given protein complex, it is, thus, possible to determine the proportions of monomers and oligomers present—whether in an organism or in a batch of medication—and which different glycosylation patterns occur and in what amounts.
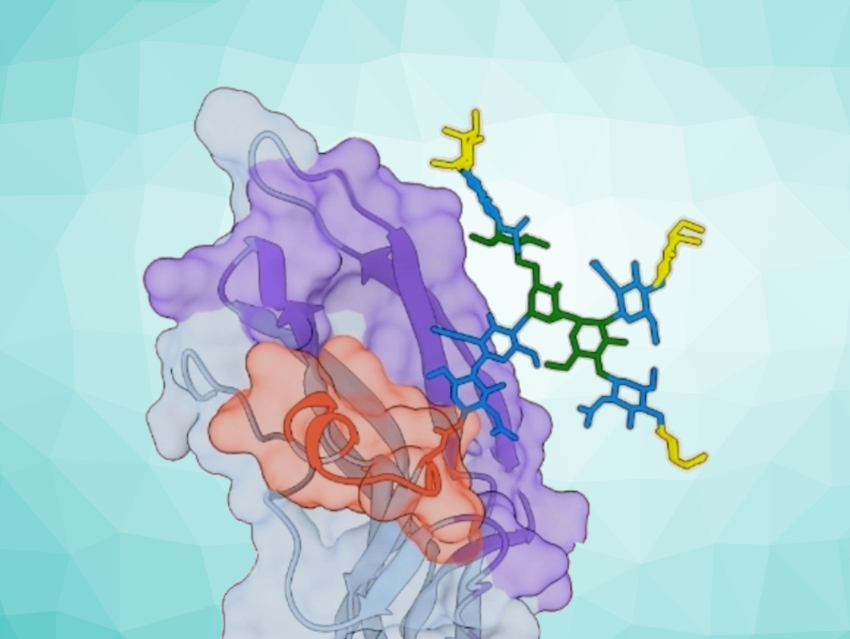
The team concentrated on glycans that are located at the interface between two subunits and can play an important role in oligomerization. They compared the results of their measurements with a theoretical model that was computed based on the dissociated subunits. This made it possible to draw conclusions about the stabilization effect of the glycans.
Therapeutic Glycoprotein Assemblies
One of the therapeutic glycoproteins the team studied was interferon-β (IFN-β), an anti-inflammatory cytokine that is used to treat conditions such as multiple sclerosis. IFN-β1a forms an asymmetrical homodimer. The MS analyses showed that most of the primary forms of both the monomer and dimer are glycosylated. However, for this cytokine, dimerization is independent of glycosylation status.
Things are different for tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), an inflammatory cytokine. Antibody-based biopharmaceuticals that neutralize TNF-α are used in cases of autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, or psoriasis. TNF-α is a homotrimer with one glycan at the interface of each subunit. The MS analyses, as well as experiments with a small molecule that disrupts the trimerization, indicated that the glycans significantly stabilize the TNF-α trimer.
The researchers also studied the follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH, follitropin), a heterodimer made of α and β subunits. Drugs based on follitropin α are used for fertility treatments. The team discovered an unusual distribution of glycans on the α subunit. One of these glycans interacts extensively with the β subunit and is clearly involved in the regulation of the dimerization.
The knowledge gained through native top-down MS experiments could help to tailor glycans in therapeutic proteins to improve their stability and effectiveness.
- Native Top‐Down Mass Spectrometry Reveals a Role for Interfacial Glycans on Therapeutic Cytokine and Hormone Assemblies,
Di Wu, Carol V. Robinson,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202213170