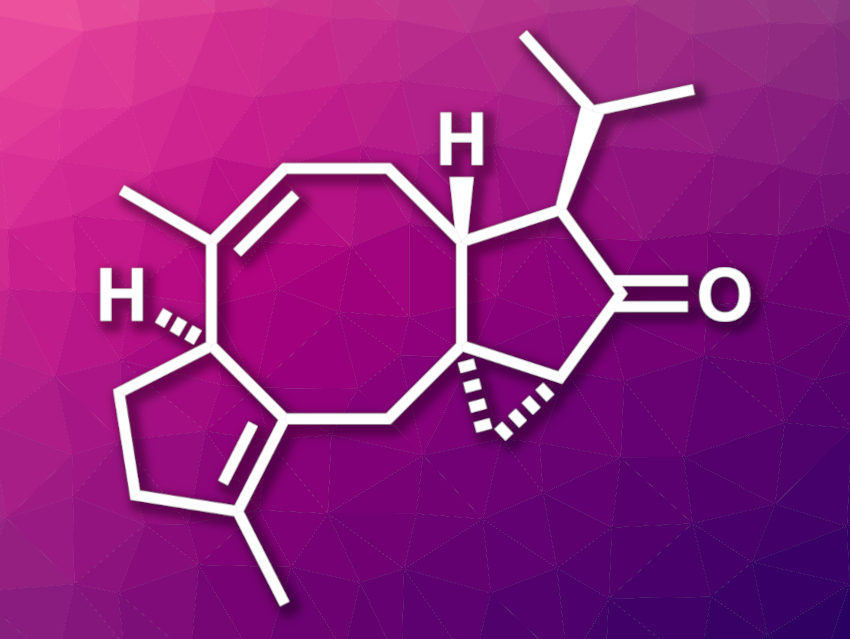
Diterpenoid natural products often have interesting biological activities and complex structures. This can make them useful in drug development and provide challenging targets for organic synthesis. Hypoestin A, for example, is a diterpenoid that shows inhibitory activity of a calcium channel that is found in nerve and heart cells. Its structure features a [5-8-5-3] tetracyclic skeleton with five stereocenters—four of them contiguous.
Chuang-Chuang Li, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, China, and colleagues have performed the first asymmetric total synthesis of hypoestin A. The team started from commercially available (R)-limonene, which was converted to a functionalized cyclopentene derivative. This intermediate was functionalized with an alkyne group and after further transformations, it was reacted with a propargylborane derivative to introduce an allenic alcohol. The alcohol was then protected using a tert-butyl(dimethyl)silyl (TBS) group.
This sequence provided the precursor for a key step: a Pauson–Khand reaction that forms the [5-8-5] tricyclic core. A reduction with diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBAL) followed by a diastereoselective Simmons–Smith cyclopropanation was then used to introduce the three-membered ring. With the tetracyclic skeleton complete, further transformations then gave the desired hypoestin A.
The synthesis required 15 steps from (R)-limonene. According to the researchers, the work represents the first use of a Pauson–Khand reaction to access synthetically challenging eight-membered ring systems in natural product synthesis. The strategy could also be useful for the total synthesis of other natural products with [X-8-5] ring systems.
- Asymmetric Total Syntheses of Hypoestin A, Albolic Acid, and Ceroplastol II,
Yong-Qiang Wang, Kunhua Xu, Long Min, Chuang-Chuang Li,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c04633



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)