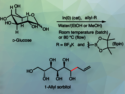
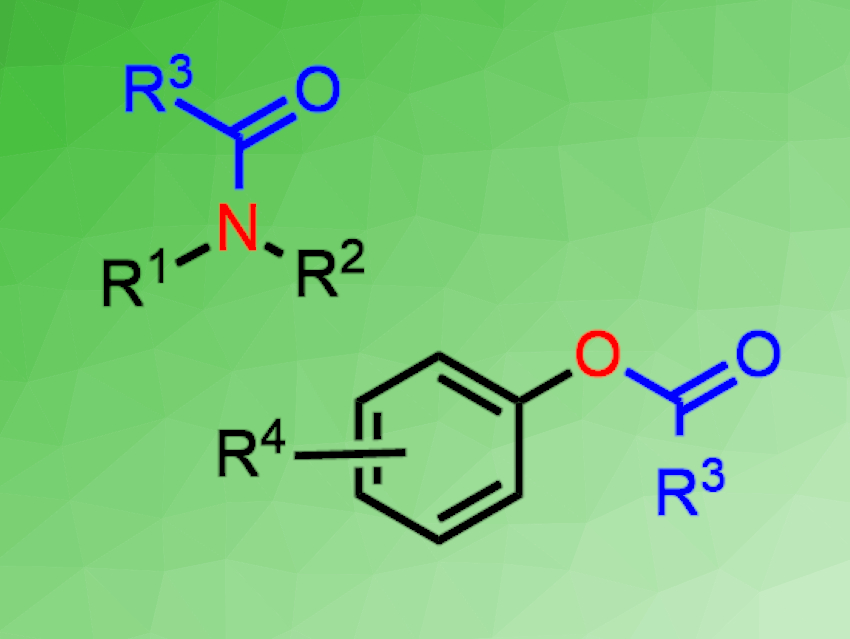
Amides and esters are widely used in organic chemistry. Their traditional synthesis involves reacting carboxylic acids or their derivatives with amines/alcohols in the presence of water-sensitive coupling reagents. Solid thioacid salts are easy to handle, transport, and store. Thus, they could be useful acylating agents, but their activation is challenging. CO2 is abundant, non-toxic, and renewable.
Yuehui Li, Lanzhou Institute of Chemical Physics, China, and colleagues have developed a CO2-promoted approach for the direct acylation of amines and alcohols using thioacid salts under mild conditions (pictured below). The team reacted different potassium thioacids with a broad range of amines at 35 °C in γ-valerolactone or with phenol derivatives at 100 °C in diethylene glycol dimethyl ether (diglyme). The reactions were performed under a carbon dioxide balloon.

The method gave various amides or esters in good to excellent yields under transition-metal-free conditions. The reaction was also used in the synthesis of valuable bioactive molecules. The work could provide a convenient approach to the synthesis of amides and esters.
- CO2‐promoted direct acylation of amines and phenols by the activation of inert thioacid salts,
Huan Wang, Yudong Li, Shaoli Liu, Mohamed Makha, Jian-Fei Bai, Yuehui Li,
ChemSusChem 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202200227

![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)