Continuous-flow reactions with heterogeneous catalysts are useful research targets due to their efficiency, safety, and low environmental impact. Enantioselective Lewis acid catalysis can be a powerful tool in the synthesis of optically active compounds. However, its application in heterogeneous catalysis and flow reactions has remained challenging.
Shū Kobayashi and Yuki Saito, The University of Tokyo, Japan, have functionalized an SiO2 support with aminopropyl silanes, followed by the addition of heteropoly acids (e.g., phosphotungstic acid or PTA) in ethanol at room temperature to form salts on the silica surface (pictured below). Chiral scandium complexes were then non-covalently immobilized—via electrostatic interactions—on the surface of the decorated silicas by mixing the complex Sc(III)-2,6-bis[(3aR,8aS)-(+)-8H-indeno[1,2-d]oxazolin-2-yl)pyridine with the support in acetonitrile.

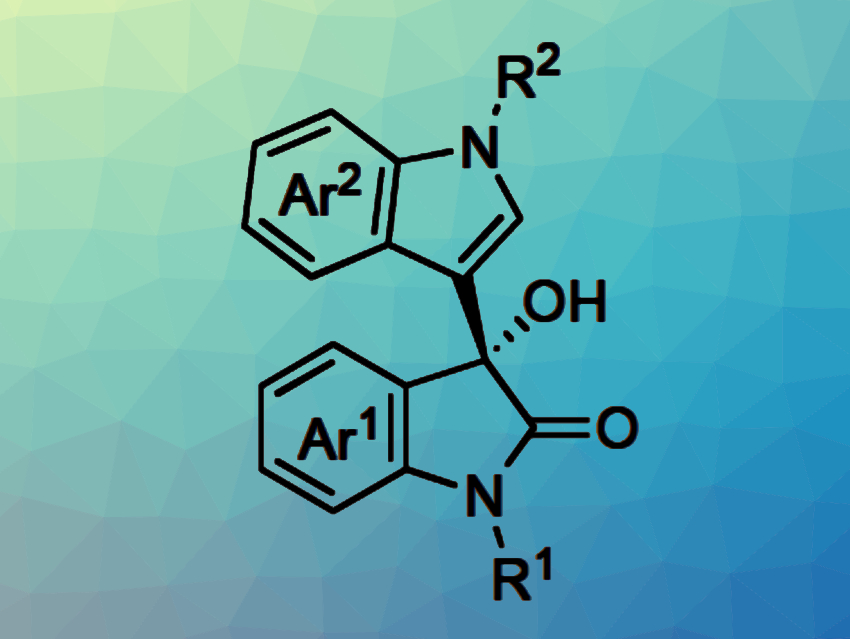
The resulting chiral heterogeneous scandium Lewis acid catalysts were used in continuous-flow Friedel-Crafts reaction of isatins with indoles (pictured). The desired products were synthesized, continuously and for hours, with high yield and selectivity. The work represents the first example of highly efficient continuous-flow heterogeneous chiral Sc-based catalysis.
- Chiral Heterogeneous Scandium Lewis Acid Catalysts for Continuous‐Flow Enantioselective Friedel–Crafts Carbon–Carbon Bond‐Forming Reactions,
Yuki Saito, Shu Kobayashi,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202112797