Organic phosphenium ions (R2P+) are intrinsically reactive species that can serve as effective activators of small molecules such as H2, N2, and H2O. However, the isolation of unsupported phosphenium ions is challenging due to their high reactivity, and stabilized, isolable phosphenium ions are less reactive as a result of their reduced intrinsic electrophilicity.
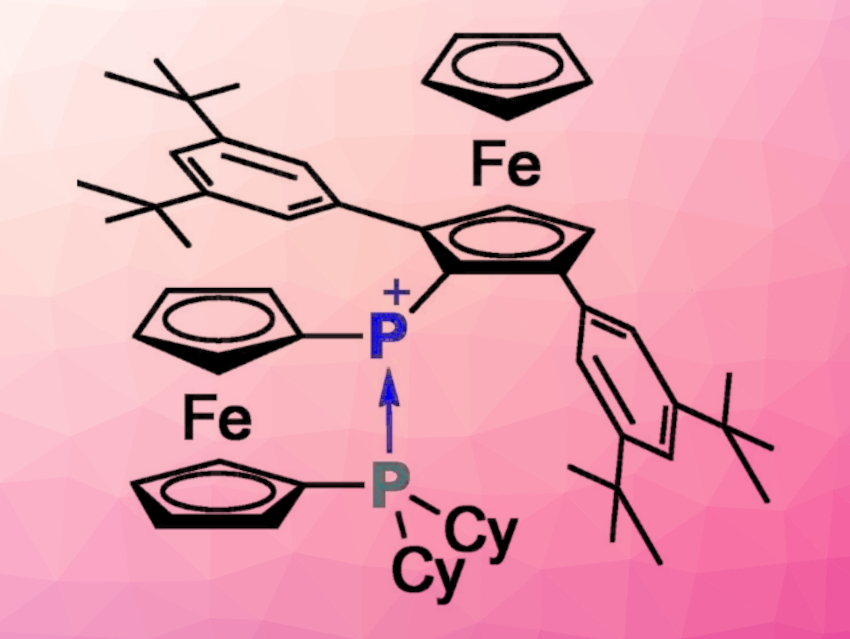
Takahiro Sasamori, University of Tsukuba, Japan, and colleagues have designed a ferrocene-based phosphenium ion with “reversible” intramolecular donor coordination, [Fc*FcPP]+ (pictured, Fc* = 2,5-(3,5-tBu2-C6H3)2-1-ferrocenyl, FcP = 1′-dicyclohexylphosphino-1-ferrocenyl). The compound was synthesized starting from 1,1′-dibromoferrocene, which was converted to 1-bromo-1′-dicyclohexylphosphinoferrocene. A reaction with n-BuLi, followed by the addition of ferrocenyldichlorophosphine Fc*PCl2, then gave the bis(ferrocenyl)chlorophosphine Fc*FcPPCl. Finally, treatment with Na[B(C6F5)4] gave the desired phosphenium salt.

The FcP group can provide both stability and reactivity at the phosphenium ion center due to its “switchable” donor coordination, caused by the rotation of the cyclopentadienyl moiety (pictured). Accordingly, the product could serve as an air-stable phosphenium ion and a potentially “bottleable” activator of small molecules.
- Ferrocene‐Based Phosphenium Ion with Intramolecular Phosphine Coordination,
Tianqing Zhang, Vladimir Ya. Lee, Shogo Morisako, Shinobu Aoyagi, Takahiro Sasamori,
Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.202100615