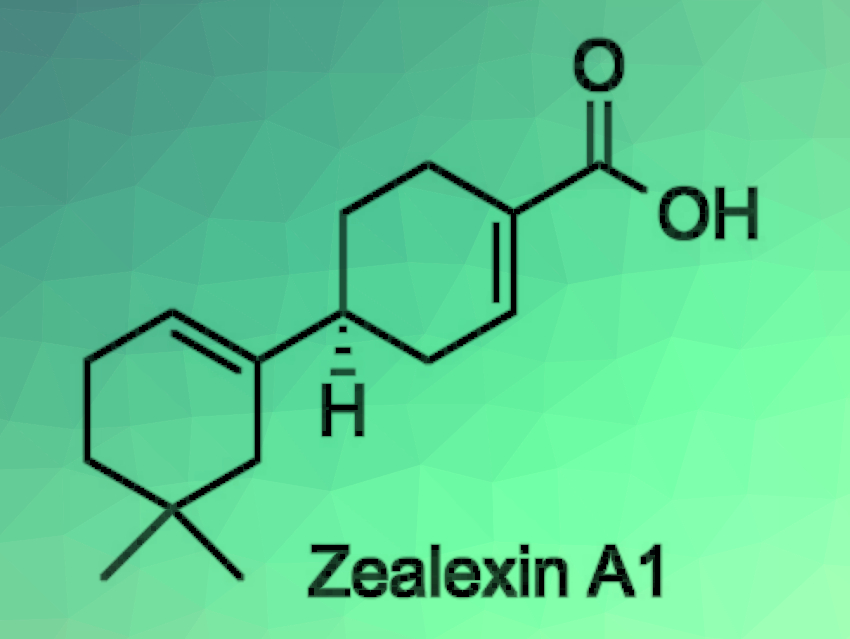
When plants suffer an attack by pathogenic fungi, they have a wide variety of defense responses. Antifungal metabolites called phytoalexins play a central role in this defense system. Zealexins are sesquiterpenoid phytoalexins isolated from maize (Zea mays) that was inoculated with pathogenic fungi. The structures of the zealexins have been elucidated through detailed analyses of their mass spectra and NMR spectra, but there has been a lack of information on the relative and absolute configurations so far.
Arata Yajima, Tokyo University of Agriculture, Japan, and colleagues have performed the first enantioselective synthesis of zealexin A1. The enantioselectivity was provided by a lipase-catalyzed enzymatic optical resolution of an allylic alcohol, followed by a Johnson–Claisen rearrangement to give a diester, and a Dieckmann condensation to construct the B-ring of zealexin A1 (retrosynthetic analysis pictured below).

The team determined the absolute configuration of natural zealexin A1 based on chiral gas chromatography (GC) analyses of synthetic and natural zealexin A1 methyl esters. The retention time of the ester of the natural product was identical to that of the synthetic (S)-isomer. Thus, the researchers determined the absolute configuration of the natural product to be S. The developed method could allow the synthesis of various zealexin-related macrocarpane-type sesquiterpenoids.
- Synthesis and determination of absolute configuration of zealexin A1, a sesquiterpenoid phytoalexin from Zea mays,
Arata Yajima, Mikaho Shimura, Tatsuo Saito, Ryo Katsuta, Ken Ishigami, Alisa Huffaker, Eric A. Schmelz,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.202001596



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)