Aromatic amines are commonly found in natural products, drugs, and dyes. Traditionally, they were prepared in multi-step sequences from nitroaromatics. More recently, metal-catalyzed amination of aromatic halides e.g. Buchwald-Hartwig (Pd) and Ullmann (Cu) couplings have been widely adopted, particularly in the pharmaceutical industry. A potentially more efficient approach would be to directly replace a C–H bond on an aromatic molecule with an amine of interest.
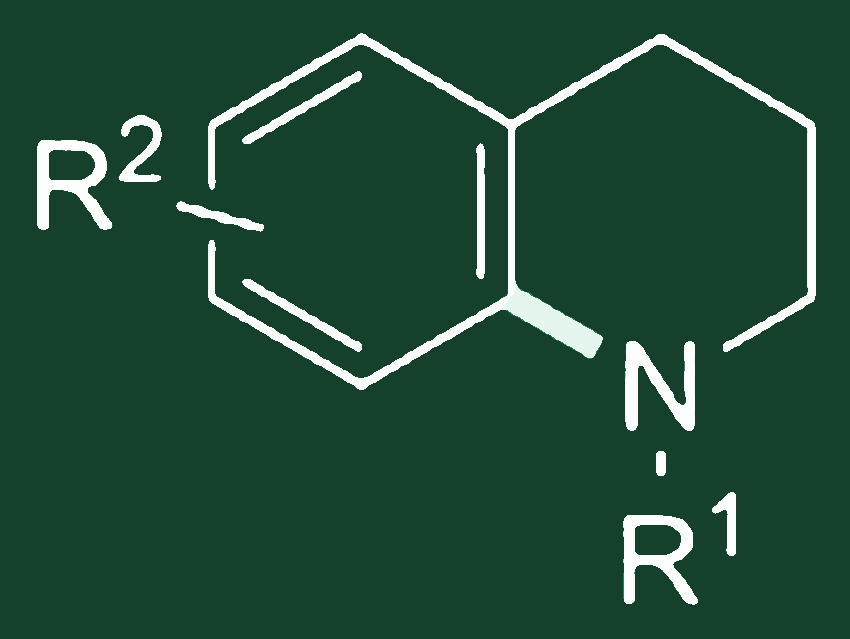
Steve Marsden, University of Leeds, UK, and colleagues have developed such a method for the direct synthesis of tetrahydroquinolines (pictured above). The aromatic C–H bonds are aminated by highly reactive aminium radicals. These are generated from readily-available N-chloroamines under catalysis by earth-abundant iron salts and CH2Cl2 as solvent.

Importantly, the chloroamine formation and aromatic amination can be carried out sequentially in a single reaction vessel, allowing for direct conversion of amines to arylated derivatives.
- Iron-Catalysed Direct Aromatic Amination with N-Chloroamines,
Gayle Douglas, Steven Raw, Stephen Marsden,
Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ejoc.201900614