Platinum-based electrocatalysts are generally regarded as the best oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) catalysts. However, they still suffer from high costs and poor stability. Recently, iron-based catalysts have been identified as promising candidates for replacing Pt-based catalysts due to their high catalytic activity and stability.
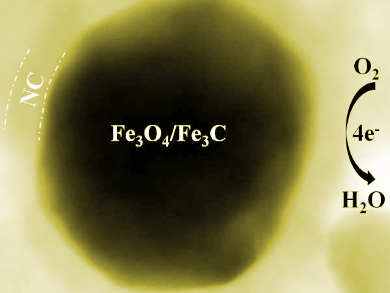
Xuhong Guo, Shihezi University, China, and East China University of Science and Technology, Shanghai, Feng Yu, Shihezi University, Lili Zhang, Agency for Science, Technology and Research, Singapore, and colleagues have developed a synthetic strategy to fabricate Fe3O4 nanoparticles which are embedded in Fe3C nanoparticles and encased in nitrogen-doped carbon shells (pictured). The hybrid nanostructures were prepared by pyrolyzing a mixture of Prussian blue and chitosan using a one-step carbon-bath method.
The obtained catalysts show an excellent ORR onset potential of 0.966 V and a limited current density of 5.59 mA cm–2, which are higher than those obtained with commercial Pt/C catalysts. It was found that the combination of materials in the hybrid structures has a synergistic effect that enhances ORR performance in an alkaline medium.
- Fe3O4/Fe3C@nitrogen-doped carbon for enhancing oxygen reduction reaction,
Mincong Liu, Xuhong Guo, Libing Hu, Huifang Yuan, Gang Wang, Bin Dai, Lili Zhang, Feng Yu,
ChemNanoMat 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cnma.201800432