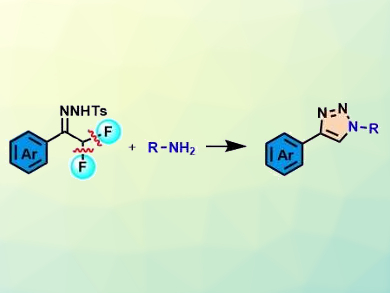
1,2,3-Triazoles have applications in chemistry, biology, and materials sciences. Cu(I)-catalyzed azide-alkyne cycloadditions have been the preferred method to synthesize these compounds. However, reactions that provide access to 1,2,3-triazoles under metal-free, oxidant-free, and azide-free conditions are rare.
Jianbo Wang and colleagues, Peking University, Beijing, China, have developed an efficient method for the synthesis of poly-substituted 1,2,3-triazoles from α,α-difluoro-N-tosylhydrazones and amines. The α,α-difluoro-N-tosylhydrazones, which can be readily prepared, react with a variety of amines in the presence of LiOt-Bu as a base to give 1,2,3-triazoles (reaction pictured). The reaction proceeds via the cleavage of two C(sp3)–F bonds.
The reaction conditions are mild and the approach has a broad substrate scope. Some of the products are obtained in nearly quantitative yield. The proposed mechanism involves the generation of an azoalkene by releasing a fluoride anion, an azo-Michael addition of aniline, a C–F cleavage, an intramolecular cyclization, and a final aromatization.
- Transition-Metal-Free [4+1] Cycloaddition for the Synthesis of 1,2,3-Triazole from α,α-Difluoro-N-Tosylhydrazone and Amine through C–F Bond Cleavage,
Qi Zhou, Zihao Fu, Lefei Yu, Jianbo Wang,
Asian J. Org. Chem. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1002/ajoc.201800514