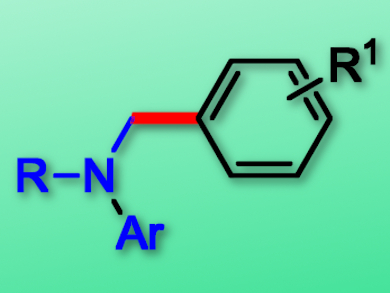
Phenols and their derivatives are widespread in nature and readily available in the chemical industry. They are attractive alternatives to aryl halides for diverse cross-coupling reactions, including C–H bond functionalization. However, as the C–O bonds in free phenols are highly inert, the preparation of phenol derivatives is required for this approach.
Da-Gang Yu, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China, and colleagues have developed an efficient arylation of aniline C(sp3)–H bonds with phenols by an in-situ activation strategy via a visible-light photoredox/nickel dual catalysis. The team used p-toluenesulfonyl chloride (TsCl) as an activation agent, Ru(bpy)3Cl2·6 H2O (bpy = 2,2′-bipyridine) as a photocatalyst, NiBr2·glyme (glyme = dimethoxyethane) as the nickel catalyst, and a blue LED to provide irradiation.
The direct use of phenols as proelectrophiles avoids the need for a purification of tosylates, is fast and step-efficient, and has a low environmental impact. The reactions tolerate a wide range of phenols and anilines and proceed in generally high yields. Moreover, these transformations feature low catalyst loading, mild reaction conditions, and easy product derivatization, and the reaction can be performed on a gram scale.
- Arylation of Aniline C(sp3)─H Bonds with Phenols by an in-situ Activation Strategy,
Yong-Yuan Gui, Zi-Xiao Wang, Wen-Jun Zhou, Li-Li Liao, Lei Song, Zhu-Bao Yin, Jing Li, Da-Gang Yu,
Asian J. Org. Chem. 2017.
DOI: 10.1002/ajoc.201700450