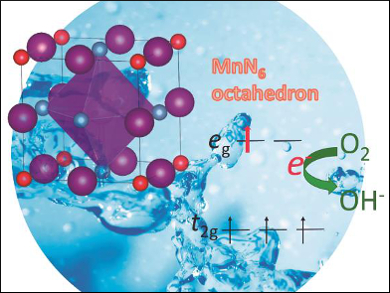
Nitrogen substitution into oxides changes their crystallographic and electronic structures. However, its role in altering catalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction has not been fully understood.
Akira Miura and colleagues, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan, have investigated how the incorporation of nitrogen into manganese oxynitrides results in their enhanced catalytic activity for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). An increase in the nitrogen content increases the oxidation state of the manganese ions from 2.4 to 3. This, in turn, reduces the overpotential of the ORR and leads to enhanced catalytic activity.
This behavior can be explained by looking at the electronic configuration of the manganese center: There is approximately one electron in an antibonding state, and the metal-nitrogen bonding has a highly covalent character, which both shift the onset potential and thus enhance the ORR. These results could be useful for the design of new catalysts.
- Nitrogen-Rich Manganese Oxynitrides with Enhanced Catalytic Activity in the Oxygen Reduction Reaction,
Akira Miura, Carolina Rosero-Navarro, Yuji Masubuchi, Mikio Higuchi, Shinichi Kikkawa, Kiyoharu Tadanaga,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016.
DOI: 10.1002/anie.201601568