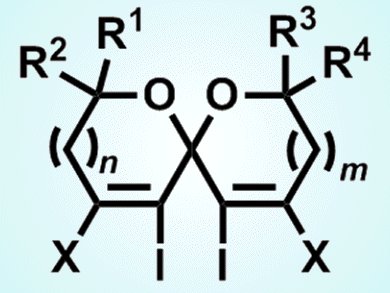
The spiroketal skeleton is important in numerous biologically significant natural products, and its synthesis is a research hotspot. However, no successful example of the preparation of the spiroketals by an electrophile-promoted cyclization has been reported until now.
Yong-Min Liang and co-workers from Lanzhou University, China, developed the synthesis of tetrahalogenated spiroketals through an iodocyclization. Reactions of symmetrical tertiary α,β-diynyl ketodiols produce tetrahalogenated spiroketals in the presence of electrophiles, such as I2, ICl, or IBr, and the same is true for tetraiodospiroketals when symmetrical primary α,β-diynyl ketodiols are used. Reactions with substrates bearing primary and tertiary hydroxy groups on both ends of α,β-diynyl ketodiols also afford the desired spiroketal products.
The team discovered that when the reactions of chiral secondary α,β-diynyl keto diol derivatives with I2 were examined,
optically active spiroketals were obtained. This spiroketalization is a synergetic process and the chiral spiroketal center is induced by intramolecular chiral alkynols.
This method might be applied to synthesize chiral ligands in Pd-catalyzed coupling reactions.
 Electrophile-Promoted Tandem Cyclization of α,β-Diynyl Ketodiols: A Facile Synthesis of Tetrahalogenated Spiroketals,
Electrophile-Promoted Tandem Cyclization of α,β-Diynyl Ketodiols: A Facile Synthesis of Tetrahalogenated Spiroketals,
Hai-Tao Zhu, Jia Wang, Zi-Hang Qiu, Li-Jing Wang, Mei-Jin Zhong, Xue-Yuan Liu, Yong-Min Liang,
Asian J. Org. Chem. 2014 3, 63–67.
DOI: 10.1002/ajoc.201300202