The presence of a chalcogen atom in a carbon chain can alter its reactivity, physical properties, and pharmacological and toxicological profile. Specifically, chalcogenophenes play important roles as semiconductors in high-performance, air-stable thin-film transistors. Moreover, they have recently been found to be pharmacologically active agents. The traditional synthetic methods for chalcogenophenes require harsh conditions involving strong bases, high temperatures, and the use of toxic polar solvents, thus limiting their large-scale application.
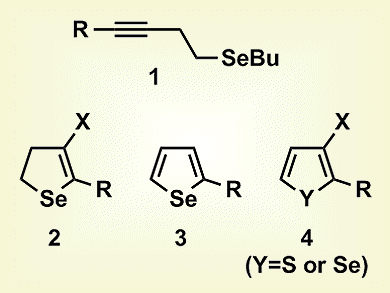
Gilson Zeni and co-workers, Universidade Federal de Santa Maria, Brazil, have developed an alternative, selective method for the synthesis of different types of chalcogenophene derivatives, specifically 4-halo-2,3-dihydroselenophenes (2), 2-substituted selenophenes (3), and 3-haloselenophenes/thiophenes (4). The reactions involved the intramolecular 5-endo-dig cyclization of homopropargyl chalcogenides (1) in the presence of commercially available, inexpensive, and relatively nontoxic copper(II) salts. At lower temperatures, 2,3-dihydroselenophenes were synthesized, whereas higher temperatures induced formation of the selenophene, with the choice of solvent affecting the substituent at the 3-position. Thus, in 1,2-dichloroethene, either 5-substituted 4-halo-2,3-dihydroselenophenes, at room temperature, or 2-substituted selenophenes, at reflux, were synthesized, but 2-substituted 3-haloselenophenes were formed in dimethylacetamide.
- Cyclization of Homopropargyl Chalcogenides by Copper(II) Salts: Selective Synthesis of 2,3-Dihydroselenophenes, 3-Arylselenophenes, and 3-Haloselenophenes/thiophenes,
Ricardo F. Schumacher, Alisson R. Rosário, Marlon R. Leite, Gilson Zeni,
Chem. Eur. J. 2013.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201302129