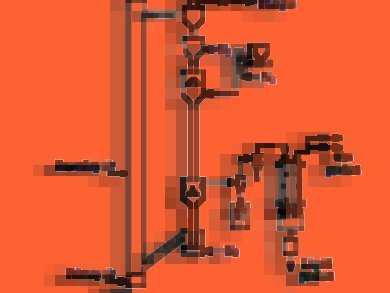
Pyrolysis is one of the promising routes for converting biomass into energy. Songgeng Li and colleagues, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, investigated the effects of acid washing treatment on the pyrolysis product distribution and product properties in a bench-scale circulating fluidized-bed (CFB) downer reactor with wheat straw as feedstock.
Acid washing treatment increases the amount of volatiles in wheat straw. This may be attributed to the dramatically increased percentage of cellulose after the treatment.
Acid washing treatment removes most of the inorganic mineral matter present in the biomass. This results in an increase in the liquid product yield and a decrease in char formation.
The liquid product from the pretreated wheat straw has relatively lower oxygen and water contents and, consequently, a higher calorific value.
CO and CO2 are the dominant components in the gaseous product, accounting for over 90 %. The CO concentration in the gaseous product from the acid-treated wheat straw is higher than that from the wheat straw while the CO2 concentration is lower. The pretreatment also produces chars with high unreleased volatiles. This indicates that the pretreated wheat straw needs a longer residence time to maximize the volatiles yield.
- Rapid Pyrolysis of Wheat Straw in a Bench-Scale Circulating Fluidized-Bed Downer Reactor,
T. Ding, S. Li, J. Xie, W. Song, J. Yao, W. Lin,
Chem. Eng. Technol. 2012, 35.
DOI: 10.1002/ceat.201200140