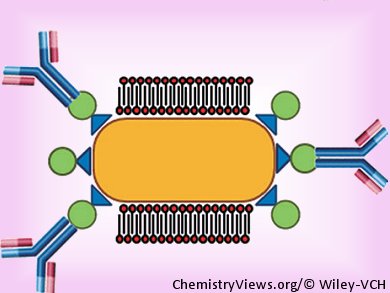
Gold nanorods (GNRs) have proven useful for imaging and biological sensing processes. Normally, GNRs are prepared using cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) but this surfactant bilayer limits subsequent easy functionalization of the nanorods.
A conceptually new method to functionalize GNRs has been reported by Tae Jung Park, Chung-Ang University, Korea, and co-workers; the figure outlines their approach.

The reserachers partially replaced the CTAB bilayer on the GNR surface with an engineered protein – a gold-binding polypeptide that was fused with Staphylococcal protein A; GBP-SpA. Traditionally, GNR functionalization is challenging because nanorods have a high tendency to aggregate. However, aggregation is avoided here by pre-incubating GNRs with activated carbon to remove the free CTAB molecules. These nanorods have been further functionalized through complexation with an antibody and the resulting hybrid used for protein detection by exploiting the change of the surface plasmon of the GNRs.
- Facile Functionalization of Colloidal Gold Nanorods by the Specific Binding of an Engineered Protein that Is Preferred over CTAB Bilayers,
Won Min Park, Bong Gill Choi, Yun Suk Huh, Won Hi Hong, Sang Yup Lee, Tae Jung Park,
ChemPlusChem 2012.
DOI: 10.1002/cplu.201200239