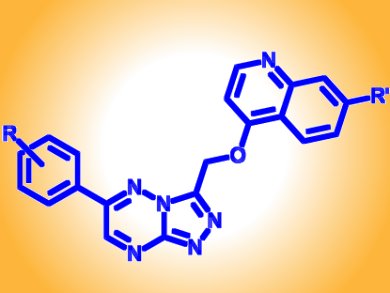
Aberrant signaling of the receptor tyrosin kinase c-Met promotes tumor development and metastasis. Strategies aimed at inhibiting c-Met ATP binding sites are among the most successful therapeutic approaches. Along this line, Fang Chen, Shangahi Institute of Materia Medica, China, and colleagues, developed novel c-Met inhibitors consisting of O-linked triazolotriazines.
The scientist synthesized two series of compounds which were able to inhibit the kinase activity at sub-nanomolar concentrations. Among them, compound 6a (pictured with R = H, R’ = OMe) displayed the highest potency and a great selectivity. It did so by inhibiting, in a dose dependent manner, c-Met phosphorylation and its downstream signaling but it was at the same time ineffective on 17 other tyrosin kinases. Consequently, compound 6a could potently inhibit proliferation of human cancer cell lines where c-Met was highly expressed and active.
Thus, highly potent and selective, compound 6a represents a novel important c-Met inhibitor.
- O-Linked Triazolotriazines: Potent and Selective c-Met Inhibitors,
F. Chen, Y. Wang, J. Ai, Z. Zhan, Y. Lv, Z. Liang, C. Luo, D. Mei, M. Geng, W. Duan,
ChemMedChem 2012, 7(7), 276–285.
DOI: 10.1002/cmdc.201200145