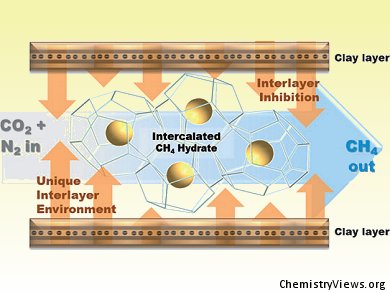
Methane hydrates from deep sea sediments could be used to provide clean energy in the next decade. Huen Lee and colleagues, Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability, Korea, extracted CH4 out of natural gas hydrate (NGH) and fixed CO2 and N2 in the NGH at the same time by using a swapping mechanism.
They found that the clay portion of underwater sediments contains significant amount of intercalated methane hydrates. By testing a mixture of CO2/N2 against pure CO2 in a high-pressure reactor they could achieve better recovery results of CH4 with the mixed gas. The team reports that 85 % of the CH4 fixed in the sediments could be recovered by the use of CO2/N2.
However, further research is needed in order to make this process suitable for industrial use. Safety questions have to be answered in order to avoid the diffusion of CO2, N2 and CH4 into the atmosphere.
Image: © Wiley-VCH
- Recovery of Methane from Gas Hydrates Intercalated within Natural Sediments Using CO2 and a CO2/N2 Gas Mixture,
Doing-Yeun Koh, Hyery Kang, Dae-Ok Kim, Juwoon Park, Minjun Cha, Huen Lee,
ChemSusChem 2012, 5 (7).
DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201100644