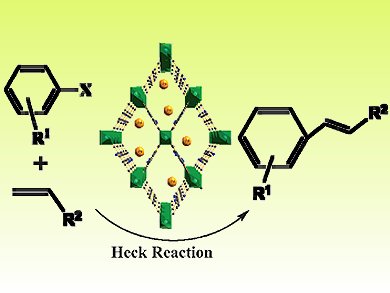
Palladium-catalyzed Heck reactions between aryl halides and olefins are traditionally carried out through homogeneous catalysis using palladium salts or organometallic complexes that are sensitive to moisture and air. To overcome such problems a heterogeneous method has been developed by Rong Cao and co-workers, Chinese Academy of Science.
The use of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for catalytic applications has not often been realized. However, these researchers used an innovative approach to prepare amine-functionalized mixed-linker MOFs based on MIL-53(Al) to immobilize palladium nanoparticles for catalytic applications. These highly stable nanoparticles show efficient catalytic activity in Heck reactions and can be easily recovered and reused. In addition, the nanoparticles were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction, N2 adsorption, transmission electron microscopy, inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
Image: © Wiley-VCH
- Palladium Nanoparticles Supported on Mixed-Linker Metal–Organic Frameworks as Highly Active Catalysts for Heck Reactions,
Y. Huang, S. Gao, T. Liu, J. Lü, X. Lin, H. Li, R. Cao,
ChemPlusChem 2012.
DOI: 10.1002/cplu.201100021
This article is available for free as part of the ChemPlusChem free trial.