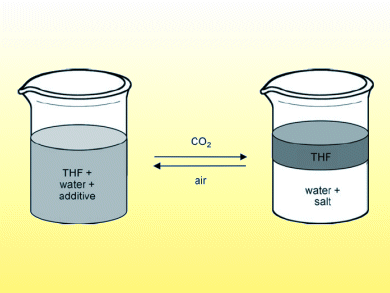
“Salting out” is a standard method for separating water-soluble organic compounds from water. Salt is added to increase the polarity of the water, forcing the organic solute out of the aqueous solution. The water that remains, however, cannot be recycled or discarded without treatment.
Sean Mercer and Philip Jessop, Queen’s University, Canada, report examples of switchable ionic strength water through addition of amines. Aqueous solutions of N,N,N’,N’-tetramethyl-1,4-diaminobutane were capable of dissolving a large amount of the test organic compound, THF. Exposing the solution to CO2 triggered a change in the aqueous solution ionic strength so that the organic compound was forced out of solution. The change was reversible through heating or sparging with N2 or air to remove the CO2, although the reverse process was incomplete.
- “Switchable Water”: Aqueous Solutions of Switchable Ionic Strength
S. M. Mercer, P. G. Jessop,
ChemSusChem 2010, 3(4), 467–470.
DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201000001