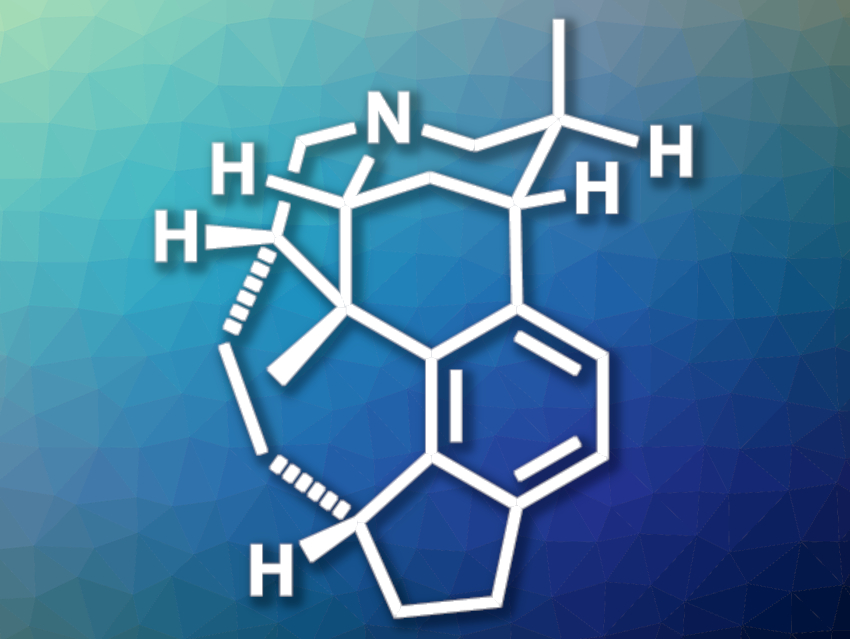
Evergreen plants from the genus Daphniphyllum have been used in traditional Chinese herbal medicines. The plants contain a large variety of triterpenoid alkaloids with polycyclic architectures and potentially useful biological activities. Daphenylline (pictured), for example, has an interesting, synthetically challenging structure.
Hai-Hua Lu, Zhejiang University, Westlake University, and Westlake Institute for Advanced Study, all Hangzhou, China, and colleagues have developed a concise asymmetric synthesis of daphenylline based on a dearomatization strategy, starting from arene building blocks. The team first prepared an ester-tethered β-naphthol, which was converted to a highly congested benzofused cyclohexenone via an oxidative dearomatization. After this key dearomatization reaction, the synthesis of daphenylline was completed via steps that include a Mukaiyama–Michael reaction and a tandem reductive amination/amidation double cyclization reaction.
The synthesis is concise and protecting-group-free. According to the researchers, the developed dearomatization strategy and other transformations used in the synthesis could also be useful for the preparation of other natural products.
- Concise Enantioselective Total Synthesis of Daphenylline Enabled by an Intramolecular Oxidative Dearomatization,
Meng-Yue Cao, Bin-Jie Ma, Qing-Xiu Gu, Bei Fu, Hai-Hua Lu,
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c01674