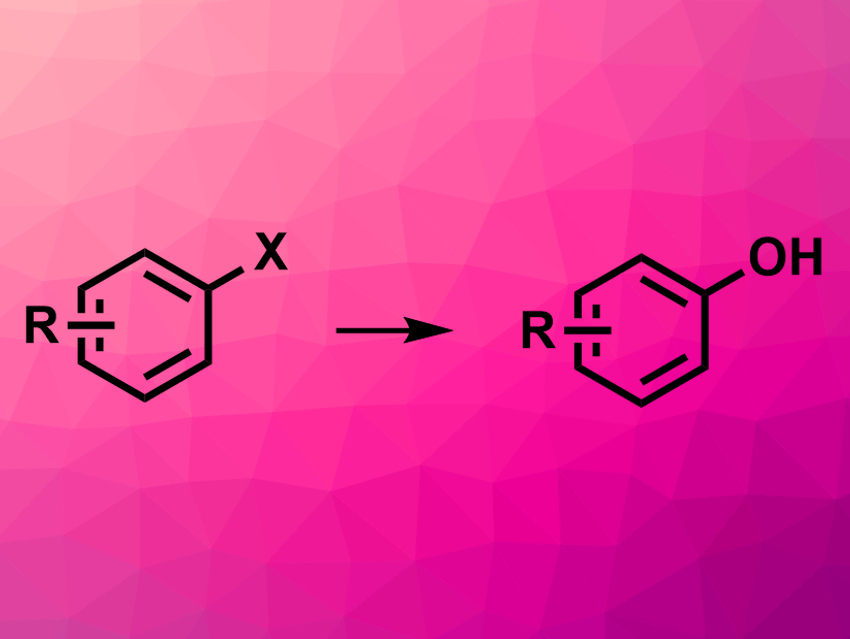
Phenols are commonly used building blocks in synthetic organic chemistry. There are several different approaches to the synthesis of phenols, but new reactions that can be run under mild conditions, have a broad functional group tolerance, use readily available hydroxide reagents, and give high yields at the same time are useful.
Zhi-Qiang Song and Dong-Hui Wang, Shanghai Institute of Organic Chemistry, China, have developed a palladium-catalyzed conversion of aryl halides to the corresponding phenols using boric acid as a low-cost, non-toxic hydroxide reagent. The team used a variety of (hetero-)aryl chlorides and (hetero-)aryl bromides as substrates and reacted them with B(OH)3 in the presence of Pd(OAc)2 as a catalyst, t-BuBrettPhos as a ligand, and Cs2CO3 as a base. The reactions were performed in N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) as a solvent at 80 °C.
The desired phenols were obtained in good to excellent yields. The reaction has a good functional group tolerance and can be used for the functionalization of complex molecules such as drug candidates or natural products.
- Palladium-Catalyzed Hydroxylation of Aryl Halides with Boric Acid,
Zhi-Qiang Song, Dong-Hui Wang,
Org. Lett. 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03069


![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)
