Eberhard Hildt, Paul-Ehrlich-Institut and German Center for Infection Research (DZIF), Gießen-Marburg, both in Langen, Germany, and colleagues have developed a vaccine platform that leads to a very good immune response (B cell and T cell response) and protection against hepatitis B in a mouse model.
Around 257 million people worldwide are suffering from a chronic liver infection, caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). In vaccines against hepatitis approved to date, the protective effect is mainly based on the formation of protective antibodies (B cell response).
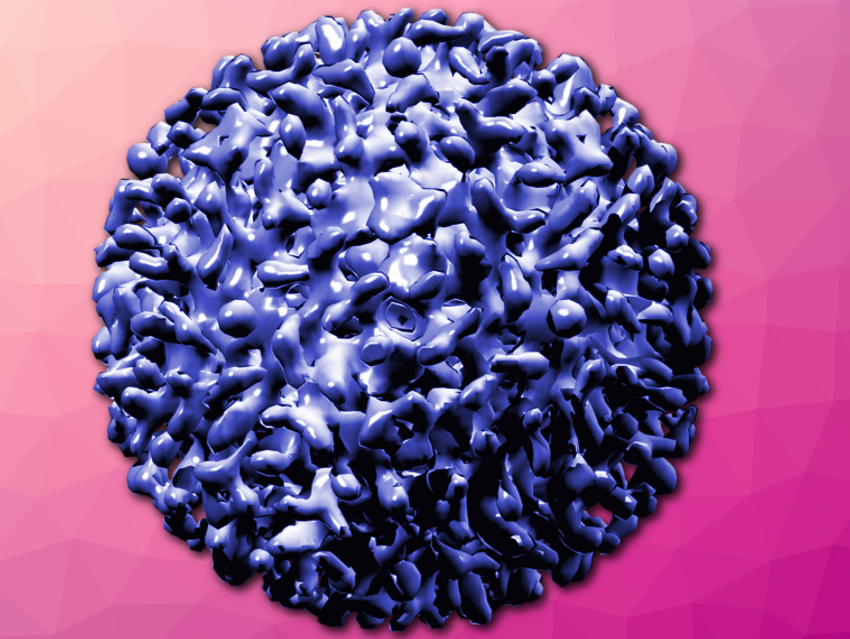
The presented vaccine platform is based on virus-like particles (VLPs) of the hepatitis B virus. The VLPs are modified capsids of the virus. Capsids are structures that envelop the virus genome. The team has merged the capsid with a so-called TLM peptide (translocation motif). This allows it to permeate cell membranes and spread throughout the body. Therefore, a possible vaccine can be administrated orally or transdermally using a plaster. By making additional modifications, the researches integrated a loading site for the antigen, against which the ummune system is supposed to develop an immune protection. This means that the VLPs function as antigen carriers.
The team loaded the capsid with a surface antigen of the hepatitis B virus. This experimental vaccine proved to be very effective in immunization experiments with mice. The mice developed protective antibodies (B cell response) and also a specific cellular immune response (T cell response) that led to the destruction of HBV positive cells. The latter might be particularly relevant for the development of a therapy against chronic infections.
The carrier of the platform can be flexibly loaded with antigens of other pathogens. Vaccine platforms are currently regarded as an important tool to shorten the response time to emerging pathogens by providing a specific vaccine.
Overall, the data indicate that cell-permeable antigen carriers, based on HBV capsids and loaded with HBV antigen, can induce a cellular and a neutralizing humoral immune response. In addition, cell permeability of the vaccine platform enables antigen transfer across several cell layers, which could allow oral or transdermal immunization.
- A new approach for therapeutic vaccination against chronic HBV infections,
Tobias Zahn, Sami Akhras, Catrina Spengler, Robin Oliver Murra, Thomas Holzhauser, Eberhard Hildt,
Vaccine 2020.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.02.063