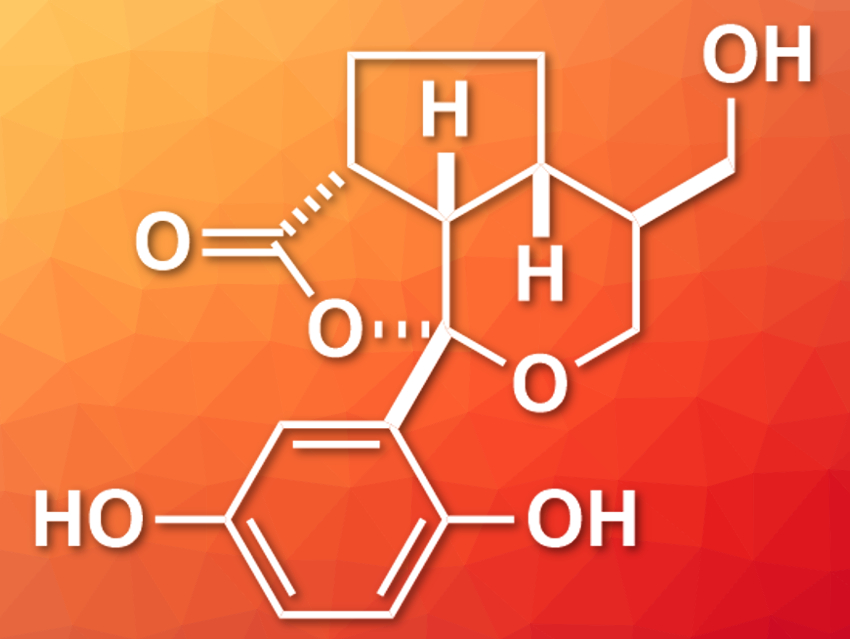
The natural products applanatumol A and B were isolated from the fungus Ganoderma applanatum in 2016 [1]. Applanatumol B (pictured) features a dioxacyclopenta[cd]indene motif and five stereogenic centers. It shows biological activity against renal fibrosis, i.e., a kidney-related disease, and could, thus, be of interest in drug design.
Hisanaka Ito, Tokyo University of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, Japan, and colleagues have performed a total synthesis of applanatumol B. They used dimethoxybenzaldehyde and 4-pentyn-1-ol as starting materials. Key steps of the synthesis involved an intramolecular Morita-Baylis-Hillman reaction for a carbon–carbon bond formation between an aldehyde and an alkene moiety, a stereoselective Michael addition, and the stereoselective formation of the tricyclic structure. An intermediate with methylated aromatic hydroxy groups was obtained as a diastereomeric mixture in a ratio of 3:1 and 88 % yield. Its conversion to a quinone allowed separation of the diastereomers via HPLC, and a reductive aromatization gave the desired product, applanatumol B.
According to the researchers, this is the first successful total synthesis of applanatumol B. The final product was obtained in 14 steps.
- Total Synthesis of Applanatumol B,
Kyohei Uchida, Yuichiro Kawamoto, Toyoharu Kobayashi, Hisanaka Ito,
Org. Lett. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01901
References
- [1] Applanatumols A and B, meroterpenoids with unprecedented skeletons from Ganoderma applanatum,
Qi Luo, Lei Di, Xiao-Hua Yang, Yong-Xian Cheng,
RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 45963–45967.
https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA05148K