Using carbon monoxide directly can be an efficient approach to carbonylation reactions. However, this usually requires transition-metal catalysts, which can be expensive and toxic. Metal-free examples of this type of reaction are rare.
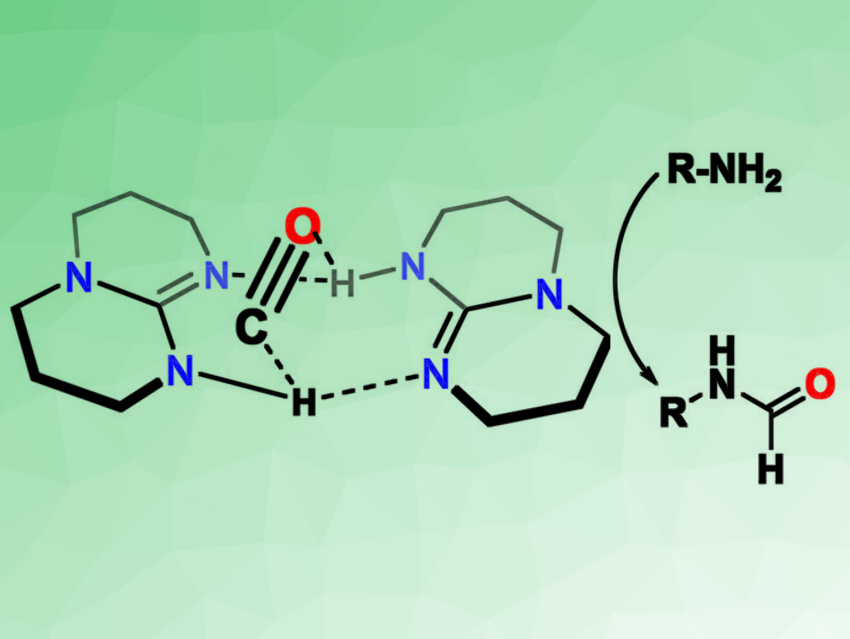
Hye-Young Janga, Ajou University, Suwon, South Korea, and colleagues have found that the bicyclic guanidine base 1,5,7-triazabicyclo[4.4.0]dec-5-ene (TBD) can activate CO by forming adducts (pictured on the left). The base can be used for a metal-free formylation of amines (pictured on the right). The team reacted TBD with CO (30 bar) and found that formylated TBD (TBD–CHO) was formed in a yield of 21 %. According to the researchers, this reaction proceeds via TBD–CO adducts.
This reactivity can be used to directly formylate amines in the presence of TBD and CO to give formamides. The formyl group of TBD–CHO is transferred to the amine during this reaction. The researchers converted a wide range of different amines under these conditions, with moderate to excellent yields depending on the substrate.
- Metal-free Carbon Monoxide (CO) Capture and Utilization: Formylation of Amines,
Hyeong-Wan Noh, Youngjoon An, Seulchan Lee, Jaehoon Jung, Seung Uk Son, Hye-Young Jang,
Adv. Synth. Catal. 2019.
https://doi.org/10.1002/adsc.201900185



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)