Oxazole groups are found in a variety of natural and biologically active products. They are interesting research targets for drug development. In medicinal chemistry, the introduction of trifluoromethyl groups is often useful to tune the properties of a drug candidate. Approaches for the synthesis of trifluoromethylated oxazoles would, thus, be useful.
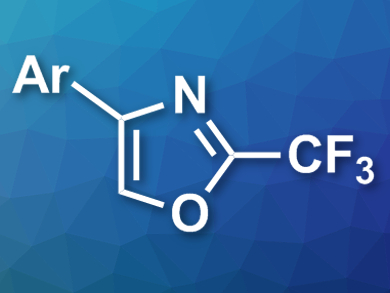
Beibei Luo and Zhiqiang Weng, Fuzhou University, China, have developed a reaction for the synthesis of 2-trifluoromethylated oxazoles (pictured), mediated by elemental tellurium. The team used oxime acetates and trifluoroacetic anhydride as substrates, tellurium as a mediator, iodine as an additive, and toluene as the solvent. The desired oxazoles were obtained in good to excellent yields.
The proposed mechanism of the reaction involves a trifluoroacetylation of oxime acetate by the trifluoroacetic anhydride, followed by a β-H elimination to give the respective enamide derivative. A single-electron-transfer (SET) reduction with Te as the reductant and an elimination of acetate then give an alkyl radical intermediate, which isomerizes to an alkoxy radical. A 5-endo-cyclization and a final oxidation step (either by iodine or a tellurium species) give the desired oxazole. According to the researchers, some of the products have fungicidal or insecticidal activities.
- Elemental tellurium mediated synthesis 2-(trifluoromethyl)oxazoles using trifluoroacetic anhydride as reagent,
Beibei Luo, Zhiqiang Weng,
Chem. Commun. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cc05670f



![Synthesis of [c2]Daisy Chains via Mechanochemistry](https://www.chemistryviews.org/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/202504_RotaxanesWithSolidStateMechanochemistry-125x94.png)