Organic compounds with fluorine substituents can be very useful, e.g., in pharmaceutical chemistry. One commonly used fluorinated group is CF3. Reactions that allow the connection of this group to sp3-hybridized carbon atoms are rare, and especially the α-trifluoromethylation of carbonyl derivatives is still challenging.
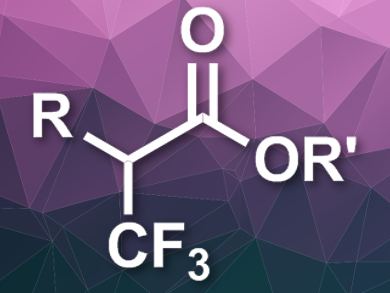
Thomas Poisson, Normandy University, Rouen, France, and Institut Universitaire de France, Paris, Tatiana Besset, Normandy University, and colleagues have developed a synthesis that provides easy access to α-trifluoromethyl esters (pictured) and starts from readily available α-chloro aldehydes. The team used an N-Heterocyclic carbene (NHC) organocatalyst, Togni’s reagent (3,3-dimethyl-1-(trifluoromethyl)-1,2-benziodoxole) as a CF3+ source, and 1,5-diazabicyclo[4.3.0]non-5-ene (DBN) as a base in a mixture of methanol and dichloromethane at 0 °C.
The desired α-trifluoromethyl esters were obtained in moderate to good yields. The proposed reaction mechanism involves an addition of the NHC catalyst to the carbonyl group of the α-chloro aldehyde, an abstraction of HCl by the base to form an enolate, an electrophilic attack of the CF3+ source at the α-position, and the formation of the ester regeneration of the catalyst via a nucleophilic attack by methanol.
- N-Heterocyclic Carbene-Catalyzed Synthesis of α-Trifluoromethyl Esters,
Fabien Gelat, Atanu Patra, Xavier Pannecoucke, Akkattu T. Biju, Thomas Poisson, Tatiana Besset,
Org. Lett. 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.orglett.8b01482