Multi-drug resistant infections are a serious problem in medicine. New antibiotics and antimicrobials are urgently needed to treat patients. Pseudomonas aeruginosa, for example, commonly infects burn wounds and causes an increased mortality risk. This pathogen is often multi-drug resistant because its outer membrane is hard to permeate. One promising class of new antimicrobials are antimicrobial peptides (AMPs). They interact with bacteria electrostatically and destabilize their membranes. This mechanism makes the development of resistances unlikely.
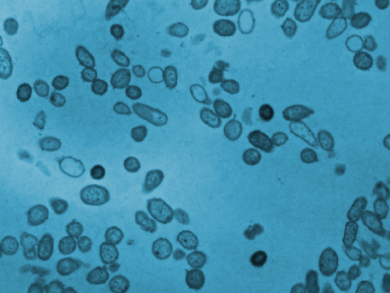
Yi Yan Yang, Institute of Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, Singapore, Weimin Fan, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, and colleagues have found short synthetic peptides which are effective against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The team used the peptides IRIKIRIK (IK8L), IRIkIrIK (IK8-2D), and irikirik (IK8D, lower-case letters stand for D-amino acids). Strains of multi-drug resistant P. aeruginosa were incubated in vitro in the presence of these peptides or antibiotics such as imipenem. After 48 hours, the researchers counted the formed bacteria colonies.
The peptide IK8L was particularly effective and inhibited the growth of bacteria in all tested strains in vitro. It performed significantly better than conventional antibiotics. The researchers also tested this peptide in mice with infected burn wounds and found improved survival rates and low systemic toxicity.
- Short Synthetic β-Sheet Antimicrobial Peptides for the Treatment of Multidrug-Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Burn Wound Infections,
Guansheng Zhong, Junchi Cheng, Zhen Chang Liang, Liang Xu, Weiyang Lou, Chang Bao, Zhan Yuin Ong, Huihui Dong, Yi Yan Yang, Weimin Fan,
Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2017.
DOI: 10.1002/adhm.201601134