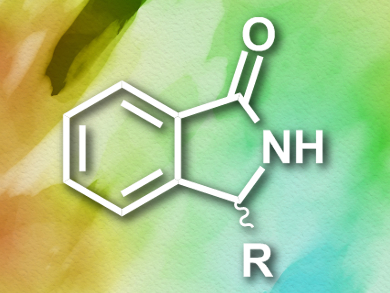
Isoindolinones (pictured) are the basis of a range of biologically active and pharmaceutically useful substances. Their uses include sedatives and anti-anxiety medications. Enantioenriched compounds show higher activity than racemic mixtures, which makes the asymmetric synthesis of isoindolinones an attractive research target. Previously, the only feasible syntheses employed chiral resolution and often had disappointing yields of only around 10 %.
Mario Waser, Johannes Kepler University, Linz, Austria, Antonio Massa, Università di Salerno, Italy, and colleagues have developed an asymmetric synthesis of substituted isoindolinones. Starting from 2-cyanobenzaldyhyde and dimethylmalonate, the team used a chiral ammonium salt as a catalyst to afford the desired N-heterocyclic building block (S)-2-(1-oxoisoindolin-3-yl)malonate in a cascade reaction. This compound could be functionalized further to give a range of biologically active derivatives.
The reaction proceeded with high yield and good stereoselectivity. In contrast to previous methods, the convenient one-pot approach is promising for large-scale applications.
- Bifunctional phase-transfer catalysis in the asymmetric synthesis of biologically active isoindolinones,
Antonia Di Mola, Maximilian Tiffner, Francesco Scorzelli, Laura Palombi, Rosanna Filosa, Paolo De Caprariis, Mario Waser, Antonio Massa,
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 2591–2599.
DOI: 10.3762/bjoc.11.279