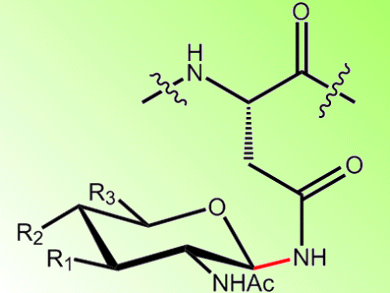
The process of N-linked glycosylation is essential for cells of higher organisms. It plays a role in a multitude of cellular functions and is performed by the membrane protein complex oligosaccharyltransferase (OST). OST catalyzes the glycosylation of asparagines via a nitrogen group, but the mechanism is unknown.
Kaspar Locher and co-workers, ETH Zürich, Switzerland, have determined the structure of OST to help understand how it operates. The team isolated and crystallized OST from the bacteria Campylobacter lari and studied it with X-ray crystallography. They see a novel fold in the transmembrane domain wherein 13 transmembrane segments are connected by external loops. One of these loops, EL5, is predicted to play an important role in OST’s activity: EL5 is expected to become ordered upon peptide binding and pins the peptide in place. This forms the catalytic site. This would enable a mechanism whereby binding of a lipid-linked oligosaccharide would result in a nucleophilic attack of the activated amide nitrogen, leading to glycosylation.
- X-ray structure of a bacterial oligosaccharyltransferase
C. Lizak, S. Gerber, S. Numao, M. Aebi, K. P. Locher,
Nature 2011, 474, 350—355.
DOI: 10.1038/nature10151