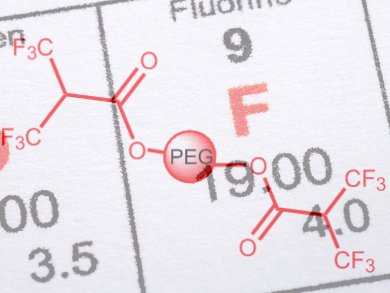
A straightforward and inexpensive route to a new class of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) agents has been developed by Maurizio Benaglia and colleagues, Università degli Studi di Milano, Italy. They synthesized hydrosoluble poly(ethylene-glycol) derivatives of 2-(trifluoromethyl)-3,3,3-trifluoro-propanoic acid.
Initial experiments gave two magnetic resonance active polymers of 2356 and 756 Dalton. The researchers found that only the lower molecular mass compound gave clear magnetic resonance images in vitro, highlighting the importance of the larger fluorine content of the smaller polymer.
- Poly(ethylene-glycol)-based Fluorinated Esters: a Readily Available Entry for Novel 19F-MRI agents
S. Rossi, M. Benaglia, M. Ortenzi, E. Micotti, C. Perego, M. Grazia De Simoni,
Tetrahedron Lett. 2011.
DOI: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2011.09.133