Natural products synthesized from fungus with affinity for opioid and cannabinoid receptors in the brain hint at new analgesics and addiction therapies.
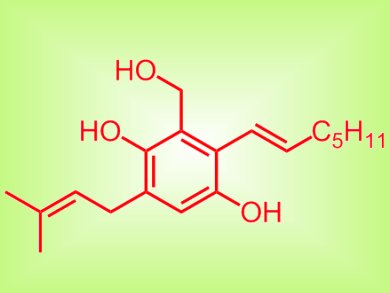
US researchers led by Stephen Cutler, University of Mississippi, have extracted two new benzyl derivatives from the fungus Eurotium repens as well as tetrahydroauroglaucin and auroglaucin by using ethyl acetate. In a high-throughput screening of the multitude of compounds isolated, they found five compounds that tested positive for binding affinity to the human opioid and cannabinoid receptors in the brain (40 % affinity).
The compounds, characterized by mass spectroscopy and NMR spectroscopy, might find use in research into diagnosable psychotic disorders or the treatment of neuropathic pain, which are modulated by agonists for those receptors.
- Benzyl Derivatives with in Vitro Binding Affinity for Human Opioid and Cannabinoid Receptors from the Fungus Eurotium repens
J. Gao, F. Len, M. M. Radwan, O. R. Dale, A. S. Husni, S. P. Manly, S. Lupien, X. Wang, R. A. Hill, F. M. Dugan, H. G. Cutler, S. J. Cutler,
J. Nat. Prod. 2011.
DOI: 10.1021/np200147c