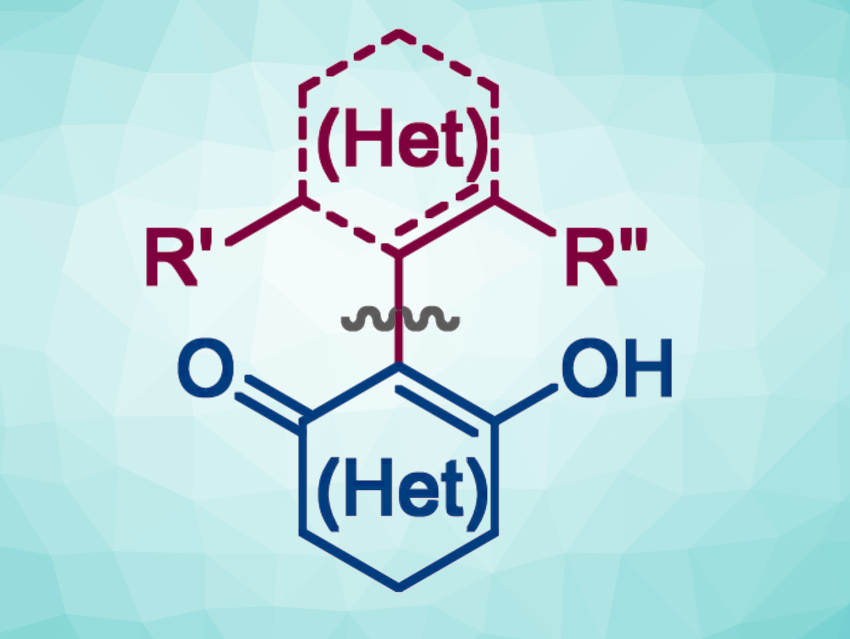
Axially chiral biaryl systems with an ortho-hydroxy group can be useful, e.g., as ligand precursors. Derivatives of such 2-hydroxybiaryls can be prepared, for example, via the arylation of (hetero)cyclic 1,3-dicarbonyls. However, this type of reaction can be challenging to achieve, in particular, for sterically hindered aryl coupling partners.
Qingfeng Du, School of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Integrated Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou, China, The Seventh Affiliated Hospital, Southern Medical University, Foshan, China, Shaoyu Mai, School of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Southern Medical University, and colleagues have developed a method for the general and catalytic α-arylation of cyclic 1,3-dicarbonyls (general product structure pictured above). The team’s approach is based on the conversion of the cyclic 1,3-dicarbonyls to cyclic iodonium ylides, followed by a rhodium-catalyzed α-arylation with arylboronic reagents (pictured below).
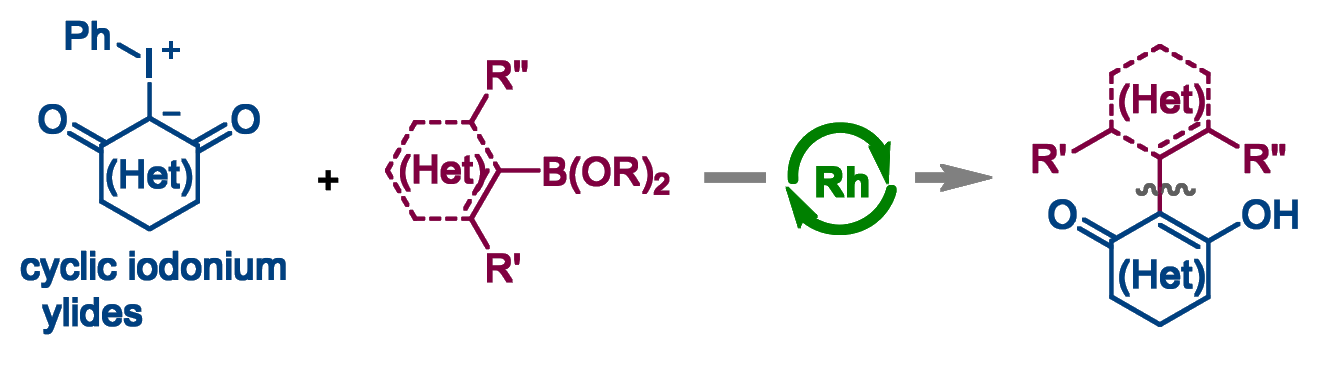
The team used [Cp*RhCl2]2 as the Rh catalyst and either water or a water/1,4-dioxane mixture as the solvent. The desired products were obtained in moderate to excellent yields. The developed approach has a broad substrate scope (over 100 examples) and the reactions proceed under mild, base-free conditions. The method provides access to useful 2-aryl (hetero)cyclic 1,3-dicarbonyl derivatives and allows for late-stage modifications.
- Catalytic and Base‐free Suzuki‐type α‐Arylation of Cyclic 1,3‐Dicarbonyls via a Cyclic Iodonium Ylide Strategy,
Mingxuan Liang, Mengling He, Zhiqing Zhong, Bei Wan, Qingfeng Du, Shaoyu Mai,
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024.
https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.202400741