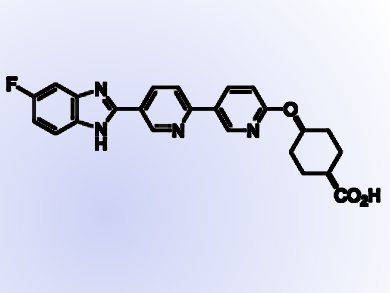
Shuwen He and colleagues at Merck in New Jersey, USA, have designed and synthesized novel inhibitors of DGAT1 (diglyceride acyltransferase 1) which have the benzimidazole chemical skeleton and contain the pyridyl-oxy-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid moiety. DGAT1 is involved in the biosynthesis of triglycerides from diacylglycerol and Acyl-CoA and thus the formation of adipose tissue.
One of the new compounds is highly selective for DGAT1 over ACAT1, acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase, which catalyzes the reversible formation of acetoacetyl-CoA from two molecules of acetyl-CoA. The team has also demonstrated efficacy at reducing triglyceride excursion in lipid tolerance tests (LTT) significantly in laboratory tests with mice and dogs where low plasma exposure was seen.
They suggest that this would reduce markedly the potential for side effects if the drug progresses to human trials in treating Type 2 diabetes and obesity.
- Potent DGAT1 Inhibitors in the Benzimidazole Class with a Pyridyl-oxy-cyclohexanecarboxylic Acid Moiety
Shuwen He, Qingmei Hong, Zhong Lai, Zhicai Wu, Yang Yu, David W. Kim, Pauline C. Ting, Jeffrey T. Kuethe, Ginger X. Yang, Tianying Jian, Jian Liu, Deodial Guiadeen, Arto D. Krikorian, Donald M. Sperbeck, Lisa M. Sonatore, Judyann Wiltsie, Christine C. Chung, Jack T. Gibson, JeanMarie Lisnock, Beth A. Murphy, Judith N. Gorski, Jinqi Liu, Dunlu Chen, Xiaoli Chen, Michael Wolff, Sharon X. Tong, Maria Madeira, Bindhu V. Karanam, Dong-Ming Shen, James M. Balkovec, Shirly Pinto, Ravi P. Nargund, Robert J. DeVita,
ACS Medic. Chem. Let. 2013.
DOI: 10.1021/ml400168h



it is good news for obese people regarding your new drug. but when the clinical trials on human will come the drug should behave properly with no side effects.