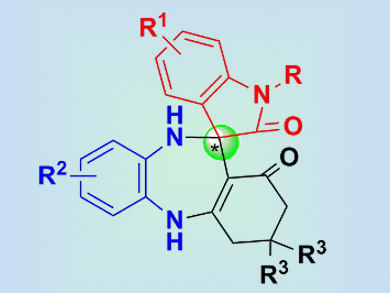
The synthesis of chiral 3,3′-spirooxindoles fused with seven-membered (or higher) ring systems (pictured) has received little attention compared with that of 3,3′-spirooxindole skeletons fused with three-, four-, five-, or six-membered rings. With great potential for bioactivity, including antimicrobial and antianxiety activities, the synthesis of such seven-membered-ring systems is highly valuable for medicinal chemistry.
Feng Shi, Jiangsu Normal University, China, and colleagues have developed the first catalytic asymmetric synthesis of a spirooxindole scaffold fused to a seven-membered benzodiazepine moiety. This transformation was performed by means of a three-component tandem reaction, catalyzed by a chiral phosphoric acid (CPA), to provide complex spirobenzodiazepine oxindoles with one stereogenic center. The tandem reaction involves a cascade enamine–imine formation and a Mannich reaction sequence, and proceeds with high yield and excellent enantioselectivity.
This strategy provides easy access to enantioenriched compounds with potential bioactivity and contributes to the field of tandem and multicomponent reactions.
- Catalytic Asymmetric Construction of 3,3′-Spirooxindoles Fused with Seven-Membered Rings by Enantioselective Tandem Reactions,
Yang Wang, Feng Shi, Xi-Xi Yao, Meng Sun, Liang Dong, Shu-Jiang Tu,
Chem. Eur. J. 2014.
DOI: 10.1002/chem.201403868