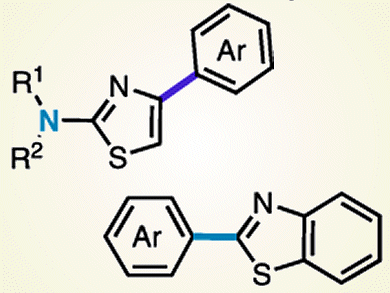
The 2-aminothiazole structural motif, which is prevalent in biologically active compounds, contains two C–H bonds and one nonaromatic C–N bond. Previously, the direct arylation of C–H bonds at the C5-position of thiazoles has been reported. However, the direct arylation of the C4–H bond or the C–N bond of 2-aminothiazoles has not yet been reported.
Junichiro Yamaguchi, Kenichiro Itami, and co-workers, Nagoya University, Japan, have successfully developed a palladium catalyst that can react with the C–H bond at the C4-position of 2-aminothiazoles. This enables a Pd-catalyzed coupling with various aryl groups by using aryl boronic acids. The team also discovered a C–N cleavage/arylation of 2-amino(benzo)thiazoles in the presence of a palladium catalyst. This transformation was achieved when the ligand was simply changed from 1,10-phenanthroline to 2,2’-bipyridine.
Further applications to medicinal chemistry and chemical biology by preparing various arylated thiazoles are the current focus of the group.
- Palladium-Catalyzed C–H and C–N Arylation of Aminothiazoles with Arylboronic Acids,
Takahiro N. Uehara, Junichiro Yamaguchi, Kenichiro Itami,
Asian J. Org. Chem. 2013.
DOI: 10.1002/ajoc.201300172